 EndoTODAY ð
EndoTODAY ð
Beginner | ESA | Schedule | OPD
Seminars | Atlas | Recent | Links
 [Visiting Endoscopy Unit at SMC]
[Visiting Endoscopy Unit at SMC]
1. Program
2. How we teach endoscopy for beginners at SMC
3. Gastroscopy box simulator training (Boxim)
4. Description exercise (DEX) - DEX Quiz
5. Case-based discussions on gastric cancer
6. Case-based discussions on gastric ESD
8. References
Learning endoscopy is not easy. In order to become an endoscopy specialist, it usually takes two years of full-time training in a dedicated training center. However, a few months of training can be enough to learn the basic knowledge and skills for a primary clinic-level screening endoscopist.
At Samsung Medican Center, we prepared the box simulator (BOXIM) workshop and the description exercise (DEX) workshop for endoscopy beginners. The BOXIM workshop is a 4 hour gastroscopy hands-on training using Koken upper GI endoscopy simulator. The DEX workshop is a 3 hour course of lectures and description training. These programs are open not only to the physicians but also to the surgeons and family medicine doctors. They are Korean language programs, but English sessions can be organized upon request.
Schedule for one week basic endoscopy course is as follows.
| One-week observation schedule (Students, General) | |||||
| Mon | Tue | Wed | Thur | Fri | |
| AM | G-BOXIM 1 (LJH) | G-ESD (LH, MBH) | Colonoscopy (KYH) At main building F4 | G-ESD (MYW) | EGD, ablation (LJH) |
| PM | EGD | G-ESD (LJH) | G-ESD (KJJ) | G-BOXIM 2 (LJH) | Colonoscopy (JDK) |
ESD training course (one week) is also available at Samsung Medical Center. It consists of (1) introductory lectures, (2) ESD observation, (3) ESD conference and ESD planning session, (4) Hands-on training using EndoGEL (artificial layer) or live pig.
If there are any questions, send me an e-mail to professor Lee at stomachlee@gmail.com.
* More information about observership program at SMC: https://www.samsunghospital.com/gb/language/english/education/observerShip.do
* Contact point: International Training Office (e-mail: dominique.cho@samsung.com)
 2. How we teach endoscopy for beginners at SMC
2. How we teach endoscopy for beginners at SMC
| SMC basic endoscopy training course (3 months) | |||
| Program | 1st month | 2nd month | 3rd month |
| On-line lecture | 


 |
KSGE lectures 1-10 | KSGE lectures 11-20 |
| Staff lecture | (1) Insertion (2) Description (3) Common GI disorders |
One point lesson | One point lesson |
| Book & Journal club | Textbook reading with tutors | Review the review | Review the review |
| Description training | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 5, 6, 7, 8 | 9, 10, 11, 12 |
| Gastric cancers 1,000 | Season 1 | Season 2 | Season 3 |
| Weekly conference | Endoscopy conference GI conference |
Endoscopy conference GI conference |
Endoscopy conference GI conference |
| Observation and hands-on | Weekly observation Simulator training |
Daily observation | Hands-on |
| Others | EndoTODAY Topic presentation 1, 2, 3 |
EndoTODAY Topic presentation 4, 5, 6 |
EndoTODAY Topic presentation 7, 8, 9 Quiz 365 |
 3. Gastroscopy box simulator training (Boxim)
3. Gastroscopy box simulator training (Boxim)
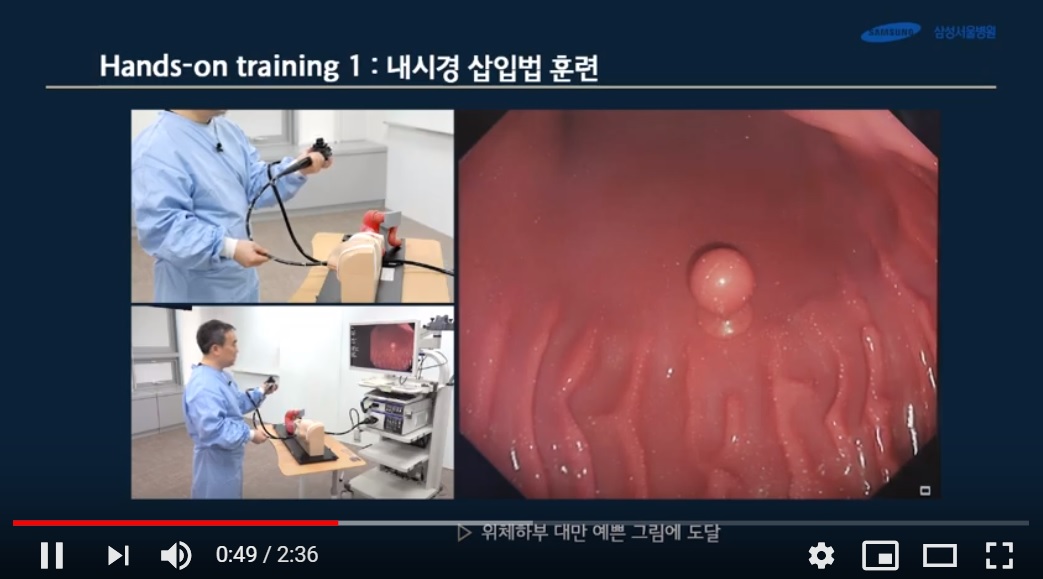
2019-1. ð Թ BOXIM ù ( κ )
Gastroscopy box simulator training guide
 4. Description exercise (DEX) and DEX Quiz
4. Description exercise (DEX) and DEX Quiz
You can learn how to describe endoscopic findings following the SMC style.
SMC style - (1) Location, (2) Size, (3) Major finding, (4) Minor findings, (5) Impression, (6) Classification
* Manual for description exercise (in Korean)
* Lectures for various topics (in Korean)
[Examples]
Example 1
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 2
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 3
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
* Classification: endoscopic classification of chronic gastritis (in Korean)
Example 4
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
* Terminology: folds of EGC, Case 1, Case 2
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 6
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 7
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 8
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 9
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 10
1) Location: 30cm from the incisor teeth
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 11
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 12
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 13
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
* Classification: endoscopic classification of EGC - Paris (2003)
Example 14
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
* Desciption example and pathology
Example 15
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
* AGC
Example 16
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example 17
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
* Typical response to H. pylori eradication in MALToma
Example 18
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
* Retroflection view of the ESD at the greater curvature of the lower body
Example 19
1) Location
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
[More cases]
[Colonoscopy]
Example C-1
1) Location: Sigmoid colon
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example C-2
1) Location: A colon and T colon
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example C-3
1) Location: Sigmoid colon
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example C-4
1) Location: mid-T colon
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example C-5
1) Location: A colon
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
Example C-6
1) Location: mid-T colon
2) Size
3) Major finding
4) Minor findings
5) Impression
6) Classification
[Description exercise quiz]
Describe the endoscopy findings follow the SMC style and then send the answer to at stomachlee@gmail.com. Professor Lee will send you the personal feedback.
 5. Case-based discussions on gastric cancer
5. Case-based discussions on gastric cancer
Case 25 - Finding gastric cancer in the background of erosive gastritis
Case 432 - flat discolorated lesion
Case 17, Case 214 - Blind area
Case 30 - Endoscopic classification of EGC
Case 58, Case 422, Case 448 - Borrmann type IV
Case 104, Case 204 - Depth of invasion
Case 43 - False negative biopsy
Case 41 - Changes after biopsy
Case 31, Case 405 - Atypia, atypical glands
Case 315, Case 420 - Remnant cancer
Case 472 - Surgery after ESD for EGC
Case 684 - Anastomosis site recurrence with peritoneal seeding
Case 445 - Rare metastasis of gastric cancer to other organs
Case 101 - Scrub typhus and gastric cancer
 6. Case-based discussions on gastric ESD
6. Case-based discussions on gastric ESD
[Indication: pathology]
Inter-observer variation on pathology
High grade dysplasia (final pathology: EGC)
Atypical gland with HGD
[Indication: gross morphology]
Would you recommend ESD or surgery? (EGC IIa+IIc with converging folds.)
Would you recommend ESD or surgery? (small flat depressed lesion with undifferentiated type histology) The patient chose surgery.
Would you recommend ESD or surgery? Ulcer and ulcer findings
Would you recommend ESD or surgery? (unclear margin and undifferentiated type histology)
Would you recommend ESD or surgery? (unclear margin and undifferentiated type histology)
[Patient aspectt]
Would you recommend ESD or surgery for a beyond indication lesion when the patient strongly want a non-surgical treatment?
[Technical aspect]
Twe nearby EGCs. One cut or two cuts?
Instrument. H type knife from Finemedix
ESD for a locally recurrent EGC
[Additional treatment and follow-up]
Local recurrence treated by surgery
Metachronous cancer in a followup loss patient
Gastric tube cancer (Deep SM invasion with positive vertical margin)
Esophageal cancer detected in the follow up endoscopy
Colon cancer and lung cancer detected in the follow up examinations.
[Cases with learning issues]
left: DLBCL (10 years ago), right: recent screening endoscopy
Surgical and endoscopic treatment of gastric cancer at Samsung Medical Center
1) EndoTODAY Endoscopy Learning Center
3) How I do it - gastric ESD (Professor Jun Haeng Lee)
© EndoTODAY Endoscopy Learning Center. Lee Jun Haeng.