 EndoTODAY 내시경 교실
EndoTODAY 내시경 교실
Beginner | ESA | Schedule | OPD
Seminars | Atlas | Recent | Links
 [Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma] - 終
[Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma] - 終
1. Introduction
7. References
1) Histologic types of the localized primary gastric lymphoma (German multicenter study, J Clin Oncol 2005)
| Histological types | Frequency (%) |
| Diffuse large B cell lymphoma with small cell component (18.1%) without small cell component (81.9%) | 59.5 |
| MALT lymphoma | 37.9 |
| T-cell lympoma | 1.3 |
| Mantel cell lymphoma | 0.8 |
| Follicular lymphoma | 0.5 |
The lymphoma cells diffusely infiltrate or completely destroy the gastric glands. The cells are large with abundant cytoplasam, vesicular nuclei, and occasionally prominent nucleoli. The centroblastic DLBCL cells have vesicular nuclei with multiple nuclear membrane-associated small nucleoli (chromatin margination), whereas the immunublastic variants display a single centrally located prominent nucleolus in most of the cells.
Transformed MALT lymphomas are chracteristically BCL2 and CD10 negative but, in contrast to MALT lymphoma, usually express BCL6. Primary gastric DLBCL, on the other hand, may be CD10 positive and a proportion are BCL2 positive. While CD10- and BCL2-positivity favor de novo DLBCL, CD10- and BCL2-negativity, commonly seen in large B cell transformation of MALToma, cannot completely exclude de novo DLBCL.
 3. Endoscopic findings of the gastric DLBCL
3. Endoscopic findings of the gastric DLBCL
여기를 참고하세요.
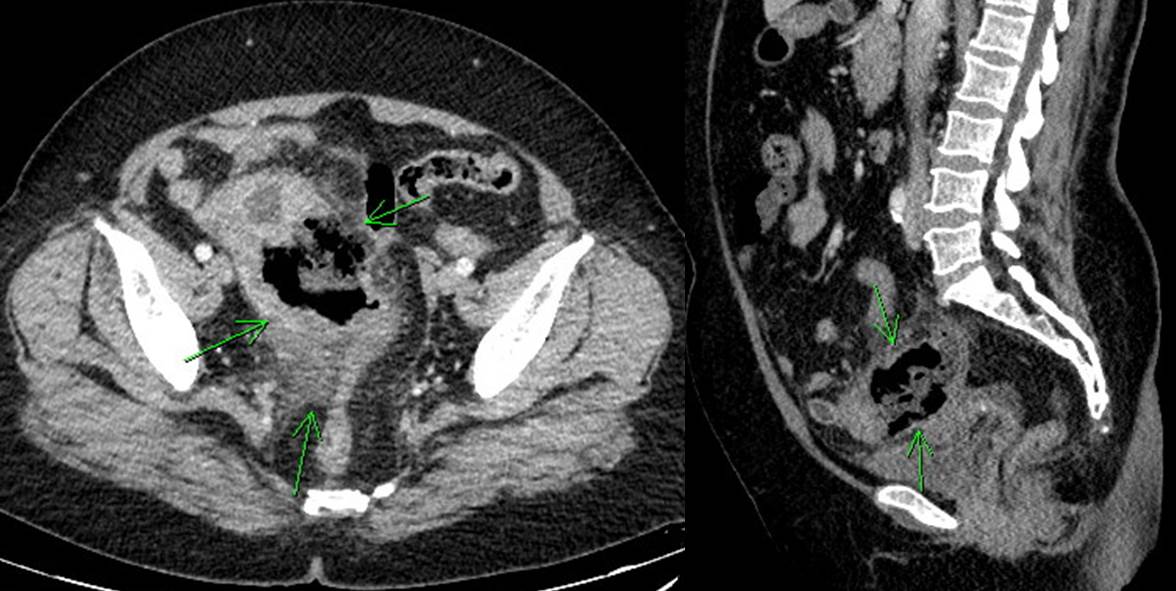
[Intussusception due to small bowel lymphoma. 소장 림프종에 의한 장중첩증]
여자 60세. 복통으로 CT 검사하여 이상소견 발견. 판독: Hepatic flexure colon에 4.9cm 크기의 malignat mass가 있으며 이것이 leading point가 되어 유도된 ileocecal intussuscption이 있음. 병변은 homogeneous한 enhancement를 보이며 ileocecal mesentery의 massive lymphadenopathy를 고려할 때 lymphoma 가능성이 가장 먼저 고려됨.
내시경 도중 hepatic flexure까지 돌출된 병변이 소장으로 밀려들어감. 소장 mass로 인한 intussusception임. 조직검사: atypical blue cell. lymphoid 혹은 NET 기원 가능성.
RLQ pain과 발열로 CT 검사를 통하여 종양이 발견되었습니다. 수술을 하였습니다.
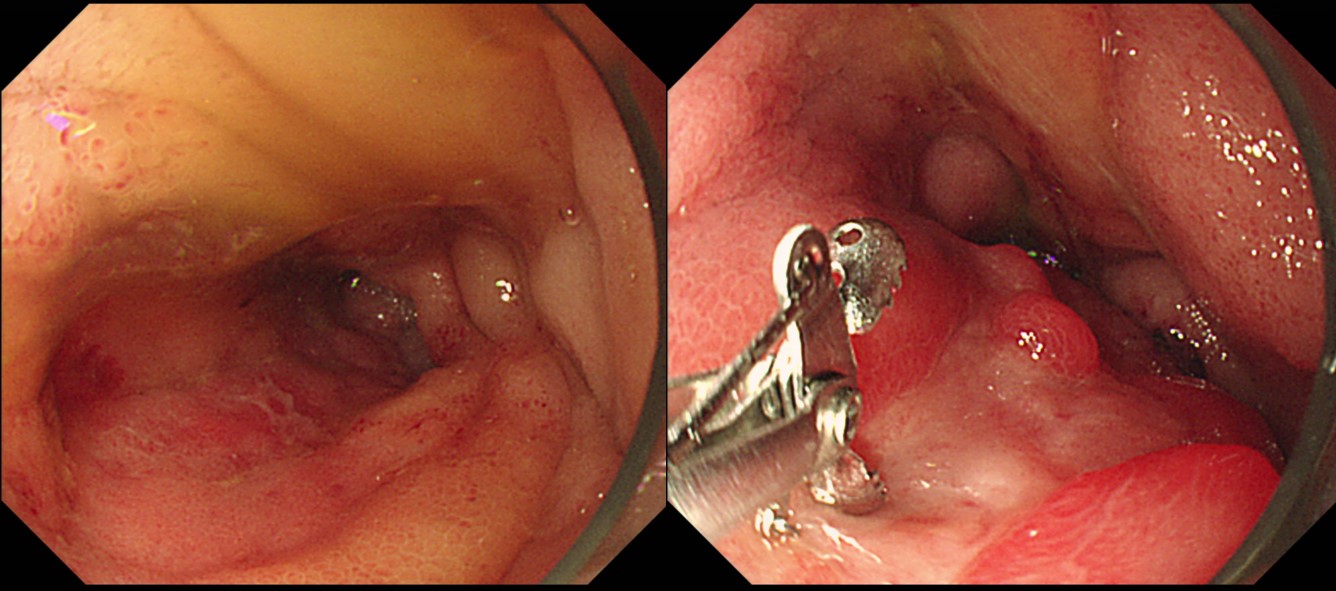
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
1. Location: small bowel
2. Gross type: ulcerofungating
3. Size: 4.5x4 cm
4. Depth of invasion: invades subserosa (pT3)
5. Resection margin: free from malignant lymphoma - safety margin: proximal, 7 cm ; distal, 4.5 cm
6. Regional lymph node metastasis : No metastasis in all regional lymph nodes(pN0)
7. Lymphatic invasion: not identified
8. Venous invasion: not identified
9. Perineural invasion: present(intramural)
10. Tumor border: infiltrative
11. Associated findings : perforation
12. Pathologic staging: pT3 N0
복통으로 시행한 CT에서 mass가 발견되어 내시경 검사에서 diffuse large B cell lymphoma가 확인되어 수술을 하였습니다.
Ascending colon, cecum, appendix, and terminal ileum, right hemicolectomy: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified, activated B-cell type
1. Location: terminal ileum
2. Gross type: bulky transmural mass
3. Size: 13x8.5 cm
4. Depth of invasion: directly invades adjacent soft tissue including bladder serosa and peritoneum
5. Resection margin: free from lymphoma, safety margin: nearest, 5.5 cm ; opposite, 5.0 cm
6. Regional lymph node metastasis : No metastasis
IC valve DLBCL (여자 60세)
1) Diffuse large B cell lymphoma의 치료  2022-9-28 삼성서울병원 종양내과 윤상은 교수님
2022-9-28 삼성서울병원 종양내과 윤상은 교수님
2) 삼성서울병원 초기 Youtube
3) 2022-11-19. 삼성서울병원 암병원 심포지엄. CAR T-cell therapy
4) [2025-1-10] CAR-T 200예 기념 Symposium. 그 동안 삼성서울병원에서 216예 치료를 하였고 median OS가 13.9 개월, ORR 70%, CR 45.8%로 global 임상연구인 Juliet 연구와 비슷하거나 약간 더 좋은 성적을 거두고 있다고 합니다. 모두 수고 많으셨습니다.
2) Diffuse large B cell lymphoma의 치료
(관리자 전용) 2022-9-28 삼성서울병원 종양내과 윤상은 교수님
© 일원내시경교실 바른내시경연구소 이준행. EndoTODAY Endoscopy Learning Center. Lee Jun Haeng